Graphic Design 101: Unlock Your Creative Power
What is Graphic Design and Why Does It Matter?
Graphic design is the art of visual communication. It uses images, typography, and color to solve problems, send specific messages, and build a unique brand identity. Professionals in this craft create visual content by applying principles of visual hierarchy and page layout to optimize the user experience.
As John Maeda once said, “Design is a solution to a problem. Art is a question to a problem.” Graphic design is all about finding those solutions visually.
Good design informs, inspires, and makes strong emotional connections with your audience. It helps businesses stand out and connect with people. This interdisciplinary field is everywhere, from the logos on your favorite products to the websites you visit. Graphic design makes complex ideas easy to understand and helps brands build trust.
As Shawn Shameli, my decade-long journey in web design and digital strategy has shown me the immense power of graphic design in creating engaging, high-performing online experiences. My focus is on blending creative design with technical precision to deliver real results.
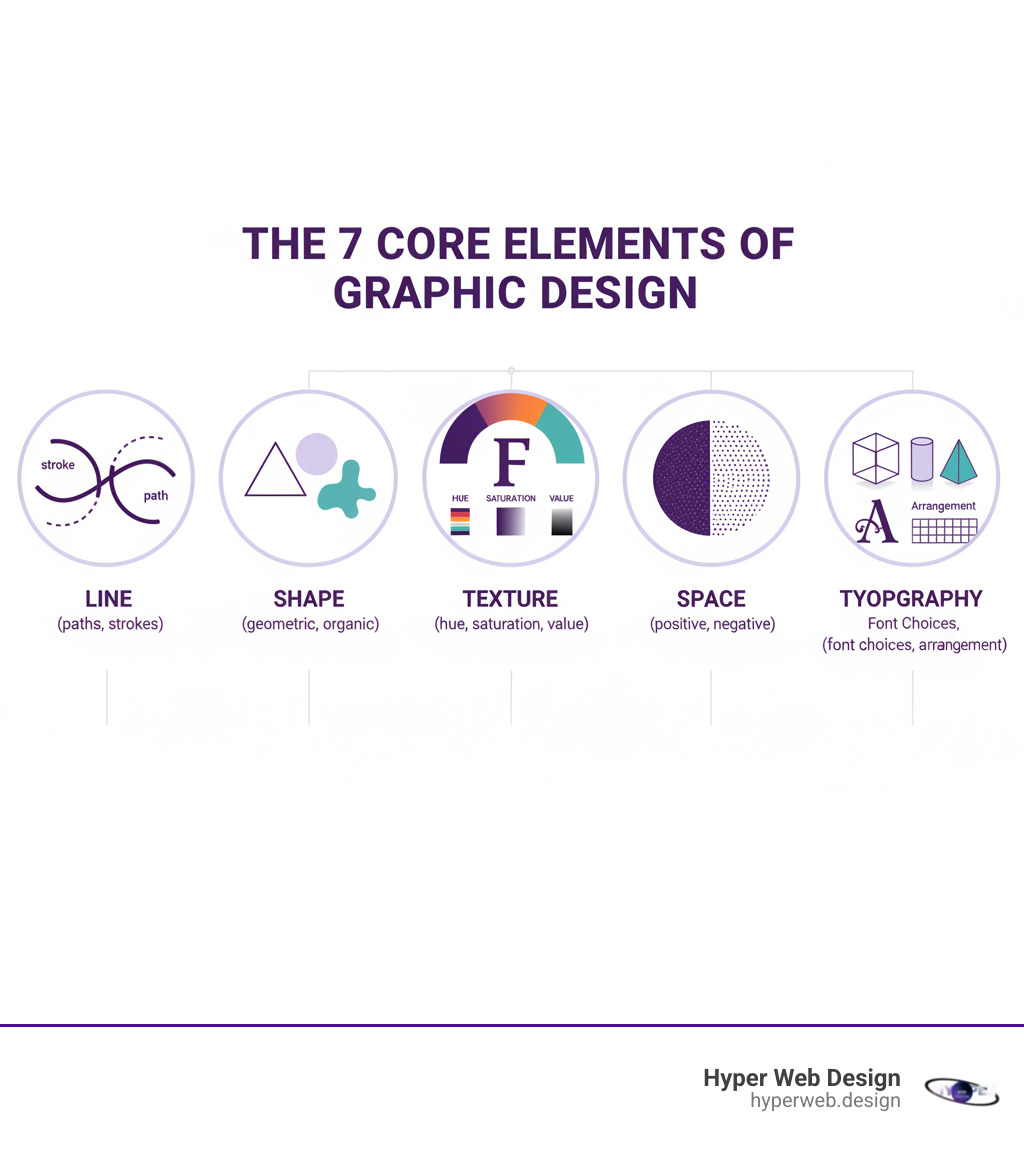
Key graphic design vocabulary:
The Core of Graphic Design: Principles, Skills, and Tools
At its heart, graphic design is about clear and impactful communication. It’s a bridge between an idea and an audience, built using a toolkit of principles, skills, and software. Designers focus on elements like visual hierarchy, page layout, composition, color theory, typography, image-making, and software proficiency to create effective visuals.
The Fundamental Principles of Graphic Design
Design principles are the guidelines for arranging visual elements effectively. They ensure designs are clear, memorable, and easy to understand.
- Balance: Distributes visual weight to create harmony, either symmetrically (even) or asymmetrically (dynamic but stable).
- Contrast: Uses differences (like light vs. dark) to grab attention, create excitement, and highlight important elements.
- Repetition: Repeats elements like colors or shapes to create consistency, unity, and a strong brand identity.
- Proximity: Groups related items together to organize information and make it easier to process.
- Alignment: Lines up elements to create a clean, professional, and orderly look, forming visual connections.
- White Space (or Negative Space): The empty area around elements that reduces clutter, improves readability, and helps guide the eye.
- Visual Hierarchy: Tells the eye what to look at first by using size, color, and placement to emphasize certain elements. You can see this in our visual web design projects.
- The Rule of Thirds: A composition trick where key elements are placed along a 3×3 grid to create more balanced and interesting images.
- The Golden Ratio: A mathematical ratio (roughly 1:1.618) found in nature that can be used to create aesthetically pleasing layouts.
Understanding these principles, as explored in resources like The Fundamentals of Graphic Design, is the foundation of effective visual communication.
A Journey Through Design History
The story of graphic design is as old as visual communication itself. Its roots trace back to ancient cave paintings and Egyptian hieroglyphs used to share information. A major turning point was Johannes Gutenberg’s invention of the printing press in the mid-1400s, which laid the groundwork for modern typography and page layout.
The Industrial Revolution created a need for advertising and commercial art. In the 20th century, movements like the Bauhaus in Germany revolutionized design education by blending art, craft, and technology. The term “graphic design” itself gained traction in the early 1900s, as detailed in a brief history of the term “graphic design”.
The biggest recent shift was the digital revolution in the 1980s. Personal computers and software moved design from a manual to a digital craft, making it more accessible and constantly reshaping how we practice it today.
Essential Skills and Tools for the Modern Designer
Success in graphic design requires a mix of creative talent, technical skill, and strategic thinking.
The Key Skills We Cherish:
- Creativity and Innovation: Generating fresh ideas and unique visual solutions.
- Communication: Telling stories visually and collaborating effectively with clients and teams.
- Problem-Solving: Analyzing challenges to design effective visual solutions.
- Understanding Your Audience: Researching user preferences to ensure designs connect.
- Color Theory Expertise: Using color to evoke emotions and match a brand’s identity.
- Mastering Typography: Choosing fonts that are readable and set the right tone.
- Layout and Composition: Arranging elements for a balanced, clear, and engaging design.
- Software Savvy: Mastering industry-standard design software.
- Time Management: Juggling multiple projects to meet deadlines.
- Persistence and Resilience: Accepting feedback and refining work with passion.
Our Essential Design Toolkit:
The Adobe Creative Suite is the industry standard for graphic design.
- Vector Graphics Editors: For creating scalable artwork like logos and icons.
- Adobe Illustrator: The go-to for creating crisp vector art that can be resized without losing quality.
- Raster Graphics Editors: For editing pixel-based images like photos.
- Adobe Photoshop: The leader for image editing, photo manipulation, and digital painting. Learn more about creating compositions with it.
- Desktop Publishing Software: For creating multi-page documents like brochures and books.
- Adobe InDesign: Our top choice for professional layouts for print and digital media.
Beyond these, tools like Figma for prototyping and basic knowledge of HTML/CSS are valuable for web-focused designers at Hyper Web Design, enabling powerful and integrated online experiences.
From Passion to Profession: Your Future in Design
The journey into a graphic design career is exciting and diverse, with many paths for creative individuals to make an impact.
Specializations and Applications of Graphic Design
Graphic design offers a huge range of specializations, each requiring a unique mix of skills.
- Branding and Identity Design: Creates the visual heart of a brand, including logos, color palettes, and style guides. This is key to a strong brand identity website design.
- Marketing and Advertising Design: Develops eye-catching visuals like social media graphics, print ads, and billboards to promote products or services.
- Web and UI (User Interface) Design: Focuses on the look and feel of websites and apps, ensuring they are attractive and easy to use.
- Packaging Design: Creates product boxes, labels, and wraps that stand out on shelves and inform customers.
- Publication Design: Lays out books, magazines, newspapers, and e-books for print and digital formats.
- Motion Graphics Design: Combines design with animation to create animated logos, explainer videos, and movie titles.
- Environmental Graphic Design: Integrates design into physical spaces through signage, murals, and museum exhibits.
- Information Design & Data Visualization: Transforms complex data into clear, easy-to-understand visuals like infographics and charts.
While related, some fields have key distinctions:
| Feature | Graphic Design | UX Design (User Experience Design) | Visual Design |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Visual communication of a message. | The overall feel and usability of a user’s interaction with a product. | The aesthetic appearance and feel of a digital product, bridging UX and UI. |
| Scope | Broad, covering print, digital, branding, advertising, and more. | Holistic, including research, wireframing, prototyping, and testing the entire user journey. | A subset of UX, focused on the visual elements like branding, color, and typography. |
| Key Questions | How do we communicate this visually? | Is this easy to use? Does it meet user needs? | Does this look good? Is it consistent with the brand? |
| Skills | Typography, color theory, layout, software proficiency. | User research, information architecture, prototyping, usability testing. | Graphic design principles, branding, UI patterns, attention to detail. |
Building Your Career Path
Becoming a graphic designer requires dedication and a smart plan.
How to Learn the Ropes:
- Formal Education: A bachelor’s degree in graphic design provides a structured foundation in theory and practice.
- Online Courses & Certifications: Platforms like Coursera and certifications from Adobe offer flexible ways to build skills and credentials.
- Self-Teaching: With discipline, you can learn through online resources, but getting good feedback is crucial.
Building Your Awesome Portfolio:
Your portfolio is your visual resume. Build it through:
- Internships: Gain real-world experience and industry connections.
- Volunteer Work: Offer your skills to non-profits to build your portfolio while helping the community.
- Personal Projects: Create passion projects to showcase your creativity and style.
- Networking: Attend events and join online groups to meet mentors and find opportunities.
Where You Can Work & What to Expect:
- In-house: Work for a single brand, offering stability and deep brand knowledge.
- Agency: Work with many clients on diverse projects in a environment.
- Freelancing: Be your own boss, offering flexibility but requiring business skills.
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) projects about 3% growth for designers from 2022 to 2032, driven by digital media. The average annual salary for graphic designers is typically between $43,000 and $66,000, with a median of $58,910 in May 2023, according to the BLS career projections. Specializing in UI/UX can lead to higher earnings.
The Future of Visual Communication
The world of graphic design is rapidly evolving with new technology.
- AI in Design: Artificial Intelligence and automation are handling routine tasks, freeing designers to focus on strategy, creativity, and adding a human touch to AI-generated concepts.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR): These technologies are creating new frontiers for design, challenging us to think in 3D and create immersive, interactive spatial experiences.
- User-Centric and Emotional Design: The focus is shifting beyond aesthetics to creating meaningful connections. Emotional design aims to make every user interaction memorable and enjoyable.
- Sustainability and Inclusivity: Designers are increasingly focused on eco-friendly practices and creating accessible digital experiences that are welcoming to all users, regardless of ability or background.
- Motion Graphics and Interactivity: Static images are giving way to dynamic, animated content that improves storytelling and user engagement in branding and digital products.
In this fast-changing world, a strong digital presence is essential. At Hyper Web Design, we blend luxurious design with smart technology to create secure, conversion-focused, and stunning digital experiences. We help your brand lead the future, not just keep up. Explore professional web design services to see how we can build your future-proof online presence.